Sasha Issenberg, nymag.com

One of Trump’s midterm rallies. Photo: Mark Peterson/Redux
The year is 2019. California’s new governor, Gavin Newsom, recently elected on a platform that included support for the creation of a single-payer health-care system, now must figure out how to enact it. A prior nonpartisan analysis priced it at $400 billion per year — twice the state’s current budget. There appears to be no way to finance such a plan without staggering new taxes, making California a magnet for those with chronic illnesses just as its tax rates send younger, healthier Californians house-hunting in Nevada and big tech employers consider leaving the state.
But Newsom is not alone. Other governors have made similar promises, and Newsom calls together the executives of the most ideologically like-minded states — Oregon, Washington, New York, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Maryland. What if they banded to create a sole unified single-payer health-care system, spreading risk around a much larger pool of potential patients while creating uniformity across some of the country’s wealthiest states?
Fifteen end up forming an interstate compact, a well-established mechanism for working together, explicitly introduced in the Constitution. They sketch out the contours of a common health-care market: a unified single-payer regime with start-up costs funded in part by the largest issue ever to hit the municipal-bond market. The governors agree, as well, on a uniform payroll tax and a new tax on millionaires and corporations set to the same rate with revenues earmarked for health-care costs. The Trump administration has already proved willing to grant waivers to states looking to experiment beyond the Affordable Care Act’s standards — primarily for the benefit of those seeking to offer plans on their exchanges with skimpier coverage. But the states can’t act unilaterally: The Supreme Court has ruled that Congress must approve establishment of any compact claiming authority that previously resided with the federal government.
Newsom pressures his friend House Majority Leader Nancy Pelosi to introduce a bill that would give the compact all federal money that flows into its constituent states for health-care costs. Pelosi’s members from Arizona and Florida balk at the proposal, which they fear would enable their states’ Republican governors to gut Obamacare protections. But there are scores more from states looking to join the compact, and their governors marshal Democratic House delegations into a bloc. The bill passes the House, with the support of tea-party Republicans eager to strike a blow against federal power.
When it reaches the Senate, the initiative comes from Republicans. In 2011, then–Texas governor Rick Perry championed a Health Care Compact Alliance, joined by eight other states seeking a “regulatory shield” against the Affordable Care Act and full control over their Medicare and Medicaid funds. By the time the Democratic bill passes the House, current Texas governor Greg Abbott has rallied more than 20 states, including North Carolina, Missouri, and Arizona, for a new version of the Health Care Compact. He also has the support of two prominent senators, Ted Cruz and Majority Whip John Cornyn. Republicans who had promised for nearly a decade to repeal and replace Obamacare can finally deliver on the promise — for 40 percent of the country.
The president sees opportunity, too. While running for president, Donald Trump called himself “Mr. Brexit,” a boast tied to his apocryphal claim of having accurately predicted the British vote to leave the European Union. Now he’s convinced, thanks largely to a Fox & Friends chyron reading BIGGER THAN BREXIT?, that an even more significant world-historical accomplishment is within reach. Trump lobbies Pelosi and Mitch McConnell to combine their bills. Trump beams at the Rose Garden signing ceremony, calling it “the biggest deal ever” as he goads Pelosi and McConnell into an awkward handshake. Historians will later mark it as the first step in our nation’s slow breakup, the conscious uncoupling of these United States.
Let’s just admit that this arranged marriage isn’t really working anymore, is it? The partisan dynamic in Washington may have changed, but our dysfunctional, codependent relationship is still the same. The midterm results have shown that Democrats have become even more a party of cities and upscale suburbs whose votes are inefficiently packed into dense geographies, Republicans one of exurbs and rural areas overrepresented in the Senate. The new Congress will be more ideologically divided than any before it, according to a scoring system developed by Stanford political scientist Adam Bonica: the Republicans more conservative, the Democrats more liberal.
Come January, we are likely to find that we’ve simply shifted to another gear of a perpetual deadlock unlikely to satisfy either side. For the past eight years, there has been no movement toward goals with broad bipartisan support: to fund new infrastructure projects, or for basic gun-control measures like background checks or limits on bump stocks. Divided party control of Capitol Hill will make other advances even less likely. For the near future, the boldest policy proposals are likely to be rollbacks: Democrats angling to revert to a pre-Trump tax code, Republicans to repeal Obama’s health-care law. By December 7, Congress will have to pass spending bills to avoid a government shutdown. Next March looms another deadline to raise the debt ceiling.
Meanwhile, we have discovered that too many of our good-governance guardrails, from avoidance of nepotism to transparency around candidates’ finances, have been affixed by adhesion to norms rather than force of law. The breadth and depth of the dysfunction has even Establishmentarian figures ready to concede that our current system of governance is fatally broken. Some have entertained radical process reforms that would have once been unthinkable. Prominent legal academics on both the left and the right have endorsed proposals to expand the Supreme Court or abolish lifetime tenure for its members, the latter of which has been embraced by Justice Stephen Breyer. Republican senators including Cruz and Mike Lee have pushed to end direct election of senators, which they say strengthens the federal government at the expense of states’ interests.
Policy wonks across the spectrum are starting to rethink the federal compact altogether, allowing local governments to capture previously unforeseen responsibilities. Yuval Levin, a policy adviser close to both Paul Ryan and Marco Rubio, wrote in 2016 that “the absence of easy answers is precisely a reason to empower a multiplicity of problem-solvers throughout our society, rather than hoping that one problem-solver in Washington gets it right.” In a recent book, The New Localism, center-left urbanists Bruce Katz and Jeremy Nowak exalt such local policy innovation specifically as a counterweight to the populism that now dominates national politics across the Americas and Europe.
Even if they don’t use the term, states’ rights has become a cause for those on the left hoping to do more than the federal government will. Both Jacobin and The Nation have praised what the latter calls “Progressive Federalism.” San Francisco city attorney Dennis Herrera has called it “the New New Federalism,” a callback to Ronald Reagan’s first-term promise to reduce Washington’s influence over local government. “All of us need to be reminded that the federal government did not create the states; the states created the federal government,” Reagan said in his 1981 inaugural address. At the time, Democrats interpreted New Federalism as high-minded cover for a strategy of dismantling New Deal and Great Society programs. Now they see it as their last best hope for a just society.
Some states have attempted to enforce their own citizenship policies, with a dozen permitting undocumented immigrants to acquire driver’s licenses and nearly twice as many to allow them to qualify for in-state tuition. Seven states, along with a slew of municipal governments, have adopted “sanctuary” policies of official noncooperation with federal immigration enforcement. Many governors, including Republicans in Massachusetts and Maryland, have refused to deploy National Guard troops to support Trump’s border policies, and California has sued the federal government to block construction of a wall along the Mexican frontier. After the Trump administration stopped defending an Obama-era Labor Department rule to expand the share of workers entitled to overtime pay, Washington State announced it would enforce its own version of the rule and advised its peers to do the same. “It is now up to states to fortify workers through strong overtime protections,” Washington governor Jay Inslee wrote last week.
In California, officials who regularly boast of overseeing the world’s fifth-largest economy have begun to talk of advancing their own foreign policy. After Trump withdrew from the Paris climate agreement, Governor Jerry Brown — he has said “we are a separate nation in our own minds” — crossed the Pacific to negotiate a bilateral carbon-emissions pact with Chinese president Xi Jinping. “It’s true I didn’t come to Washington, I came to Beijing,” said Brown, who is often received like a head of state when he travels abroad. Around the same time, Brown promised a gathering of climate scientists that the federal government couldn’t entirely kill off their access to research data. “If Trump turns off the satellites,” he said, “California will launch its own damn satellite.”
Brown’s successor Newsom comes to office just as Californians may be forced to reckon with how much farther they are willing to take this ethic of self-reliance. Since 2015, a group of California activists have been circulating petitions to give citizens a direct vote on whether they want to turn California into “a free, sovereign and independent country,” which could trigger a binding 2021 referendum on the question already being called “Calexit.”
During the Obama years, it was conservatives who’d previously talked of states’ rights who began toying with the idea of starting their own countries. “We’ve got a great union. There is absolutely no reason to dissolve it,” Rick Perry said at a tea-party rally in 2009, before adding: “But if Washington continues to thumb their nose at the American people, you know, who knows what may come out of that?” Perry’s lieutenant governor, David Dewhurst, met with members of the Texas Nationalist Movement on the opening day of a legislative session. Right after this year’s midterms, the would-be leaders of the breakaway republics of Texas and California met at a secessionist conference in Dallas.
In 2012, the White House website received secession petitions from all 50 states; Texas’s was the most popular, with more than 125,000 signatures. (A counterpetition demanded that any citizen who signed one of the secession petitions be deported.) Two years later, Reuters found that nearly one-quarter of Americans said they supported the idea of their states breaking away, a position most popular among Republicans and rural westerners. [JB emphasis]
If we are already living in two political geographies, why not generate a system of government to match?
Liberal regions have tended to go bigger with their secession fantasies: Why spin off one’s own state when you could split the whole country and gain the resources and manpower of like-minded compatriots? After John Kerry’s loss in the 2004 election, a homemade digital graphic migrated across the pre-social internet. On it, the states that had cast their electoral votes for Kerry were labeled “the United States of Canada”; George W. Bush’s became “Jesusland.” After Trump’s victory, those memes graduated into op-eds, including from others who would have to acquiesce in the fantasy. “Is it time for Canada to annex Blue America?” a columnist in the Canadian news magazine Maclean’s asked last year.
The fact that anyone with Photoshop can cogently cleave the country in two is a credit to the hardening of a once-fluid political map. Over half the states have cast their Electoral College votes consistently for one party in every presidential election since 2000. In 2016, those states all picked Senate winners from the same party as their presidential picks as well. But as three British geographers concluded in a 2016 article about spatial polarization, that’s not just a feature of the Electoral College map. Whether measured by county, state, or region, the partisan divide has grown since Bill Clinton’s first election: Red places have grown redder (at least in their presidential votes), blue places bluer. In 1992, 38 percent of Americans lived in “landslide counties,” which went for a presidential candidate by a margin of 20 percentage points or more, the Times has reported; in 2016, the number reached 60 percent.
This partisan homogeneity is shaping state governments too. Thirty-six capitals are now dominated by a single party that controls the governorship along with both houses of a legislature; for the first time in more than a century, only one state legislature in the country, Minnesota’s, will be split between two parties. If we are already living in two political geographies, why not generate a system of government to match?
Or so goes the fantasy. There’s no real groundswell of support for shrinking the United States. Surveys have shown that two-thirds of Californians oppose independence, and not only because the Calexit movement’s lefty critiques of Trump do not align with its righty origins. (A co-founder of the California Independence Campaign, Louis Marinelli, is a former anti-gay-marriage activist who last year sought permanent residence in Russia.) When a candidate from the Alaskan Independence Party, which had been founded with secessionist ambitions, actually won the governorship in 1990, he turned out to be tepid on the question of sovereignty. (Sarah Palin once attended an AIP conference, and her husband, Todd, became a member.) Local movements elsewhere, whether the left-leaning Second Vermont Republic or South Carolina’s right-leaning Third Palmetto Republic, have never transcended stunt. Among institutions, only the Libertarian Party has ever endorsed the position that states should be freely able to secede.
History gives us few examples of successful peaceful secessions. In the ones we do have, national identity rather than ideological differences seem to be at the root of the fissure. (The Confederate States of America would have been a notable anomaly.) When states split in the 20th century, the Australia-based scholars Peter Radan and Aleksandar Pavkovic have pointed out, there were always deep underlying fault lines of language, religion, or ethnicity. None of the three multinational states created between the two world wars — the Soviet Union, Yugoslavia, or Czechoslovakia — survived until the end of the 20th century.
Recent votes in Scotland and Quebec have modeled the way that secession in a developed country during years of peace can become just another political question.
Even with widespread fatalism about the American project, there is not an obvious way to dissolve our union. Rewriting the Constitution’s balance of power would require levels of political coordination that seem far beyond the country’s existing leadership. Chances of a civil war are remote, and it is hard to visualize a series of events that could prompt a peaceable dissolution of the union. After the Civil War, the Supreme Court ruled that states have no right to unilaterally secede. The U.N. Charter recognizes the “self-determination of peoples,” but clearly intends the latter to mean well-defined racial or ethnic groups and not, say, a collection of persons who want stronger gun-control measures. Other countries might be wary of recognizing spinoff American states for fear of the precedent. Would China vote to admit California to the United Nations if it set up Tibet or Taiwan to demand the same treatment?
And yet, if the desire to secede were to grow, recent votes in Scotland and Quebec have modeled the way that secession in a developed country during years of peace can become just another political question — one debated relatively civilly, voted on democratically, without attendant allegations of treason or sedition. (Spain’s government has been less forgiving of what it calls an unconstitutional independence referendum held last year in Catalonia.)
There is at least one mechanism by which a sort of soft breakup may be imaginable — and it’s already found within the Constitution. The document introduces the prospect of one state entering into a compact with another. States have created interstate compacts to maintain common standards, like the Driver’s License Compact that 47 DMVs use to exchange knowledge on traffic scofflaws. Most have been used for neighboring jurisdictions to handle common resources, like the Atlantic Salmon Compact that permits New England states to manage fish stocks in the Connecticut River Basin. (Eleven states have signed on to a National Popular Vote Interstate Compact, to disregard the Electoral College, but it would require a number equal to 270 electoral votes to take effect.)
Interstate compacts have rarely been applied to controversial topics. Yet to a paralyzed Congress, and a president without any deeply held views about state-federal relations, they could prove an appealing vehicle to restless factions on both the left and the right. It may be time to take the country apart and put it back together, into a shape that better aligns with the divergent, and increasingly irreconcilable, political preferences of its people — or at least to consider what such a future might look like, if for no other reason than to test our own resolve. An imagined trial separation, if you will. Or perhaps in contemplating a future apart we might stumble upon a few ideas for some new way to live together after all.
So let’s return to our hypothetical spring of 2019. After Governor Newsom’s successful health-care deal, lobbyists and think tanks promote compacts for all their pet issues, and Congress — which would be unable to find bicameral majorities for any other substantive legislation — obliges. The Public Lands and Environmental Compact Act gives the states huge leeway to set environmental regulations and manage national parks on their lands, and the Labor and Workplace Compact Act permits states to draft new workplace and employment standards. There’s a Housing Compact Act, an Immigration Compact Act, and an Agriculture Compact Act, which allows the states to take all the money that would come to their citizens as farm subsidies and food stamps as block grants with the ability to set their own rules. Trump giddily signs them all.
While the states could generate new partnerships for each policy area, they choose to harden their alliances. As they link their safety nets, the Newsom-led states agree to fully synchronize their tax codes so that they could end a race-to-the-bottom competition for residents and companies. Once they do, Nevada pulls out from the compact, unwilling to implement an income tax on its citizens. Washington, on the other hand, quickly amends its state constitution to permit an income tax for the first time.
Seeking his own symbol of integration, Abbott unveils the new Free States Open-Carry Permit, along with new laws ensuring the right to bear arms in schools, churches, and government buildings across his alliance. Newsom and Abbott jointly lobby Congress to grant them the right to manage the Social Security funds generated by workers in their regions. Abbott wants to allow citizens to control their retirement portfolio, while Newsom wants to experiment with moving some trust-fund money from the Treasury bonds to new public-investment vehicles that will support climate-friendly technology.
To kick off the Federation Era, the two governors meet on the steps of the United States Supreme Court for a photo op. Shaking hands, the men and their attorneys general pledge not to support any legal challenge to the other’s authority for two decades. All sides have an interest in permitting their new experiment to play out for a while without any unnecessary uncertainty from the courts. The states can’t stop others from suing over the constitutionality of their moves, but they want to send a message to a conservative Supreme Court that state officials are channeling the political will of 250 million Americans, all with Congress’s express consent.
The most vocal opposition comes from fixtures of the Washington, D.C., Establishment and permanent bureaucracy, which fear a permanent loss of power. Both Fox News and MSNBC, on the other hand, herald the New Era of Good Feelings. For the first time ever, Gallup records three in four Americans declaring themselves satisfied with the way things are going in the United States — a supermajority that cuts across partisan and demographic divides.
Over the first two decades of the Federation Era, the alliances remained relatively stable, with only occasional changes in state status. Virginia quit the Progressive Federation of America early because it felt it would lose leverage to defend the interests of the federal employees who live there. Montana nearly pulled out of the Alliance of Free States when it looked like it might be forced to abandon its closed-shop work rules to match its right-to-work sister states. Florida’s internal politics are driven by perpetual debate over whether the state stood to benefit by joining either federation; Alaska no longer has a Democratic Party and Republican Party but has entirely realigned along a Pro-Fed and Anti-Fed axis.
The states that did not join a federation remained governed by Washington, where largely status-quo policies from the early-21st-century remain in place. Some are in the neutral zone, as it is known, owing to principled independent-mindedness (New Hampshire), some by ideological paralysis (Wisconsin), and some because they are happy setting their own rules (Delaware). Power, however, resides in the neutral zone. Since each of the two federations cast Electoral College votes as a bloc, by tacit understanding, any viable national candidate has to hail from the unaffiliated states. (After producing four in a row, Maine changed its official slogan to “Mother of Vice-Presidents.”) Yet with the Legislative and Executive branches largely hobbled from policy-making for much of the country, this offers minor satisfaction. It is said to be a bleak joke around the White House that the only job of the president in peacetime is to inquire daily about the health of the Supreme Court’s oldest member.
By 2038, the Progressive Federation of America is being run from a former administrative building on the campus of the University of New Mexico. The federation was initially governed by commissioners appointed by governors and state legislatures. To avoid establishing a permanent bureaucracy, the governors refused to establish a dedicated base, instead rotating its chairmanship across the members for a year at a time. Lobbyists loved having the capital in San Francisco, were less enthused when New York decided it could boost the local economy by chairing its meetings in Buffalo.
The abandoned campus in Albuquerque is an inadvertent monument to one of the Blue Fed’s earliest successes. The federation’s state universities initially integrated to secure basic economies of scope and scale: linking their library collections and banding together in search of greater buying power for their energy needs. After a few years, the states agreed to set in-Fed tuition for all public universities to zero. New Mexico took the boldest step. It dismantled its public-university system after determining it was more efficient to cover travel expenses for New Mexicans studying in California or Colorado than to manage its own schools, even continuing to pay lifetime salaries for its tenured professors when they were placed in jobs at new sister schools. The New Mexico regents decided to deplete the remainder of the university’s $450 million endowment to dramatically increase teacher pay for the state’s primary-school teachers. New Mexico’s public high schools are now seen as some of the country’s finest.
At first, the task of the Federation commissioners was framed as simple technocracy, implementing the will of state governments. They strengthened regulations to protect workers and set a uniform $18 minimum wage across the zone, with some cost-of-living adjustments to raise the sum in New York, San Francisco, and Boston. Federation taxes have steadily risen as federal rates fell to cover its reduced obligations. Many wealthy Blue Fed residents now pay more in annual taxes to the federation than to Washington. The high-quality cradle-to-grave services those taxes fund have come to define existence across the Blue Fed, from guaranteed public preschool to lifelong medical coverage with no co-pays or deductibles, and have incubated a highly skilled workforce and some of the most impressive life-expectancy rates in the world. (Dental care continues to depend on a system of private insurance.) It was a source of pride when the Blue Fed’s generous higher-education system started drawing large numbers of middle-class families to leave southern cities for northern ones.
As soon as one crosses the border into the Alliance of Free States, whether over the Wabash River from Illinois to Indiana, or the grasslands that stretch across the Iowa-Missouri border, the difference between the two federations’ sense of identity becomes immediately visible. A popular decal showing an outline of the Red Fed’s borders — with a column of prairie states rising like an extended middle finger from the clenched fist of Texas — resides on bumpers and car windows as a defiant declaration of a newly defined region’s honor.
Over the first decade of its existence, Red Fed leaders found their purpose unwinding the domestic reforms of Franklin Roosevelt, Lyndon Johnson, and Barack Obama and with them much of the 20th-century regulatory state. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration, Environmental Protection Agency, and Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration all saw their staffs gutted, left incapable of enforcing whatever rules did remain on the books. An alphabet soup of government agencies, Bill Kristol tweeted, had become a savory bone broth.
The National Labor Relations Board withered in the Red Fed, along with New Deal rules that blocked companies from interfering in employee efforts to win collective-bargaining power. The shift set off a return to the fierce business-labor battles of the Gilded Age, most visible in the emergence of new firms founded by Blackwater and Black Cube alumni, known as the Blackertons, that specialize in aggressive digital surveillance and online-misinformation campaigns against union organizers.
The effective elimination of most environmental and employment regulations proved irresistible to manufacturers. Boeing announced it would stop making capital investments in its Seattle-area factory and begin to shift jet assembly to a new plant in Covington, Kentucky. Factories relocated from China to be closer to the American consumer market and avoid import tariffs. Unemployment in parts of the Red Fed fell below 2 percent and the region briefly reached 5 percent growth — each several times better than Blue Fed indicators — leading conservative economists to praise the Red Miracle.
It was not just manufacturing and resource extraction that boomed in the Red Fed. As soon as the Blue Fed established its single-payer system, medical specialists began taking their practices to states where they wouldn’t be subject to the Regional Health Service’s price controls or rationing. Sloan Kettering now treats New York as little more than an administrative base; the majority of its hospital rooms are in Texas. Johns Hopkins considered closing its medical school when nearly half the faculty decamped en masse to Baylor. Wealthy Blue Fed residents willing to pay out of pocket now invariably travel to Houston when they want an immediate appointment with a specialist of their choice. The arrivals area at the George Bush Intercontinental Airport is packed with chauffeurs from van services run by clinics supported by specializing in such medical tourism.
Auctions of public lands across the interior west, along with the privatization of the Tennessee Valley Authority, generated a quick gusher of cash. Vowing not to let the new government wealth create more bureaucracy, Red Fed leaders deposited it all in a Free States Energy Trust Fund that would pay out an annual dividend to every adult and child in the region — a no-strings-attached cash transfer of hundreds of dollars per year. The Southern Baptist Convention encouraged its members to tithe their dividend checks directly into new aid societies to help the least fortunate. The most popular charitable cause has been a relief society to aid religious conservatives in the Blue Fed seeking to migrate to the Red Fed.
The boom in manufacturing and energy jobs on one side of the border and the guarantee of free government-sponsored education and medical care on the other created an incentive for families to split — with one spouse working (and paying taxes) in the Red Fed and the other, usually with children in tow, collecting benefits in the Blue Fed. (Remo, which pitched its app to investors as “Venmo for remittances,” became the fastest-growing tech company on the Fortune 500.) Sociologists are starting to worry that what they call the “split-family phenomenon” will become a hallmark of 21st-century life in North America, with its effects growing more pronounced as federation policies continue to diverge.
Reaction to Blue Fed culture drives much Red Fed governance. When the Blue Fed opened a gleaming new visitor center at Yosemite, the Red Fed moved to privatize all the concessions at Yellowstone. The Blue Fed’s expansive affirmative-action protocols inspired the Red Fed to abolish all HBCU-specific education programs so that primarily white institutions could compete equally for the funds. After Illinois led a Blue Fed initiative to upgrade its rail service, the Red Fed ended all cooperation with Amtrak, even adjusting gauge size along the Mississippi River to prevent passage of passenger trains from one side to another. As a backlash to the Blue Fed’s net-neutrality rule, the Red Fed imposed the Online Fairness Doctrine, which permits internet providers to slow upload and download speeds for content they determined was in violation of “community standards” or that offends a company’s religious beliefs. Across large swaths of the Red Fed, the only way to log into Grindr is via VPN.
These culture-war skirmishes instilled a strong sense of Red Fed identity, and the economy was doing so well that few noticed the slow exodus of tech entrepreneurs and high-skilled creative professionals who had once clustered in Austin and North Carolina’s Research Triangle. Only when the Supreme Court ruled that a compact-wide abortion ban did not place an undue burden on reproductive freedom because Red Fed residents could travel for free services in the Blue Fed did it become evident that conservative social policy would impede efforts to diversify the Red Fed economy beyond natural resources and heavy manufacturing. Amazon’s list of candidate cities to house its HQ14 did not include a single one in the Red Fed.
Each federation is the other’s largest trading partner, but they increasingly assume the posture of rivals. When the Blue Fed imposed a controversial excise tax on all products or services generated by companies that could not prove they paid their employees at least $18 per hour, the Red Fed saw it as a de facto tariff on its goods. It retaliated by placing its own excise tax on domestic wine, which led the Red Fed to deepen its trade ties with Chile and Argentina. That was a short-term diversion, but prompted a deeper examination of how economically dependent one federation had grown on the other’s internal policies. A Blue Fed requirement that certain freight classes travel only by all-electric truck fleets had nearly doubled the cost of transporting products to the interior west. Frequent work stoppages by West Coast longshoremen emboldened by their labor-friendly administration affirmed a strategy agreed to by titans of Red Fed industry: They needed their own Pacific port.
Red Fed leaders negotiated a deal with Mexican authorities for operating control of the Port of Lázaro Cárdenas, in Michoacán state, investing some of its energy trust funds. A new terminal, staffed by American Customs officials, connects directly with a spur of the Kansas City Southern railroad. There, nonunion laborers load ships with minerals mined through the American West, including lithium and soda ash, heading largely to East Asia, and unload bananas and smartphones from Ecuador and China heading for the landlocked states of the Red Fed without ever once passing through Blue Fed territory.
And then came the first humanitarian crisis. When the families of West Virginia workers started overloading schools and hospitals across the border in Hagerstown, Maryland, the Blue Fed began to impose residence requirements for many of its social services. That didn’t stop the migrants, but it led them to cluster in border towns as they waited out the six months required for eligibility. The conditions were often dire. Tent cities around Palm Springs saw the first American measles outbreak in a generation, and in the Spokane bidonvilles, dozens of children froze to death during a harsh winter.
Those tragedies set off a reckoning that has prompted an identity crisis for the Blue Fed’s leaders and citizens. On one side, fiscal experts say the Nordic-style welfare state that the Blue Fed has established is unsustainable if it just ends up as an unchecked provider of services to some of the Red Fed’s neediest cases. On the other side, some of the progressive activists who played crucial roles building early support for the health-care compact argue that the Blue Fed has an obligation to promote its values even beyond its borders. The debate rages across the region: What obligation do they have to other Americans who have democratically chosen to pursue a very different way of life?
The federations had a gentlemen’s agreement not to drag federal authorities into their disagreements, but the nature of their conflicts made that impossible. Once the Blue Fed declared itself a “sanctuary region” and invited undocumented immigrants elsewhere in the United States to seek refuge, Red Fed leaders threatened to erect internal border controls on state lines. The Blue Fed backed down, publicly revoking its invitation, but only after the Red Fed agreed to jointly lobby Congress to create a series of regionally restricted work visas.
The federal government remains the enforcer of the country’s citizenship laws, agent of its foreign affairs, controller of its national defense, and manager of its monetary policy. But it grew increasingly impossible to perform any of those roles neutrally, and many of the country’s democratic institutions were not designed to balance the competing interests of two geopolitical rivals.
When the Federal Reserve raised interest rates to stop the Red Fed’s economy from overheating, it pushed the rest of the country into recession, prompting the Great Lakes to lead the first successful campaign to have the Federal Reserve Board removed from office. When Hurricane Rigoberto came through the Gulf of Mexico, leaving large portions of Houston underwater for months — the first trillion-dollar natural disaster, at least when the cost of the subsequent malaria outbreak is included — the Red Fed demanded a bailout from the federal government. Blue Fed politicians said it would be “moral hazard” to do so, given that most of the damage was traced to a Red Fed decision to privatize the Houston Ship Channel and entrust the buyer, a Qatari sovereign-wealth fund, with upkeep of the Galveston Seawall and the levee networks of surrounding southeastern Texas counties.
The Pentagon lost its authority to act as a nonaligned arbiter of the national interest. Once cartels seized control of the Red Fed’s Mexican container port, taking hostage 17 retired Texas Rangers working on a private security force, the Defense secretary mobilized West Coast National Guard units to support an Army Rapid Deployment Force, along with Marines and Navy seals. Oregon’s governor balked, announcing that he would not permit his troops to “be used as muscle for the Red Fed’s imperial adventures.” The Supreme Court ruled that National Guard units had to follow the commander-in-chief’s orders, and the Oregon guardsmen headed south, but the incident polarized foreign-policy positions in new ways. When, months later, intelligence agencies issued a report pinning the crash of the western renewable-energy grid on a North Korean cyberattack, Red Fed cities saw some of their largest mass protests in years, all against a rush to war. Nearly 100,000 people gathered in Indianapolis’s Monument Circle, chanting “No blood for solar.” By the time of the South China Sea Crisis, Congress had grown so paralyzed along federation lines that it was impossible to assemble a majority in favor of any declaration of war.
Leaders overseas have become eager to exploit what they see as the United States’s political weakness. As concerns about climate change have grown more dire, other countries have become intent on punishing dissenters from the international order, and the Red Fed is now a global villain. The European Union agreed to pre-clear for entry all crops produced under the Blue Fed’s GMO-free agriculture policy, while Red Fed imports are subjected to a lengthy and costly quarantine. China announced most-favored-region trade policies that would give Blue Fed exporters an advantage over domestic rivals when selling into the Chinese market.
These trade-related conflicts squeeze Illinois, which wants to export Caterpillar tractors to China under favorable conditions but lags behind West Coast and New England states in transitioning to GMO-free agriculture. Although a founding member of the Blue Fed, Illinois at times felt geographically isolated, surrounded by Red Fed or neutral states. Illinois withdrew from the Blue Fed and helped to form the Great Lakes Federation, which stretches from Philadelphia to Des Moines and up to Duluth, with a permanent capital in Chicago. As the 20-year judicial truce is about to expire, the Midwest controls the balance of power in a Congress that may be forced by the Supreme Court to revisit some of its earliest assumptions about returning power to the states.
There is another real-life contemporary example of a semi-secession: Brexit. It, too, began as little more than a thought experiment. What if we could reject a far-off governing structure that no longer seems responsive to our interests in favor of local authority that can more closely match our aspirations and sense of identity as a people? There must have been something thrilling about getting to cast a vote for self-determination.
Yet those who are now forced to make that reverie real are pulling back from their former self-confidence about it. Just last week, the Tory official serving as Secretary of State for Exiting the European Union admitted he “hadn’t quite understood the full extent” to which British commerce was “particularly reliant on the Dover-Calais crossing,” and that new trade barriers could impact the availability of consumer goods in stores. Instead of just leaving Europe, as he encouraged his compatriots to do during the 2016 campaign, Dominic Raab now insists on “a bespoke arrangement on goods which recognizes the peculiar, frankly, geographic, economic entity that is the United Kingdom.
As it was for a majority of Britons, it is easier to imagine breaking up the United States than figuring out how to make it work — whether through bold new policies or merely a functioning version of consensus politics. The seeming inelasticity of our system of governance also guarantees a security and predictability that we take for granted. Some of the lessons Europe is being taught under the stress of the Brexit crisis — that a single currency requires a unified economy, or that a lack of internal borders can’t work if no one can agree on what should happen at the outer one — are ones Americans might better learn from fantasy than from experience.
Dividing the Assets
A snapshot of what the nation would look like if it cleaved in three today.*
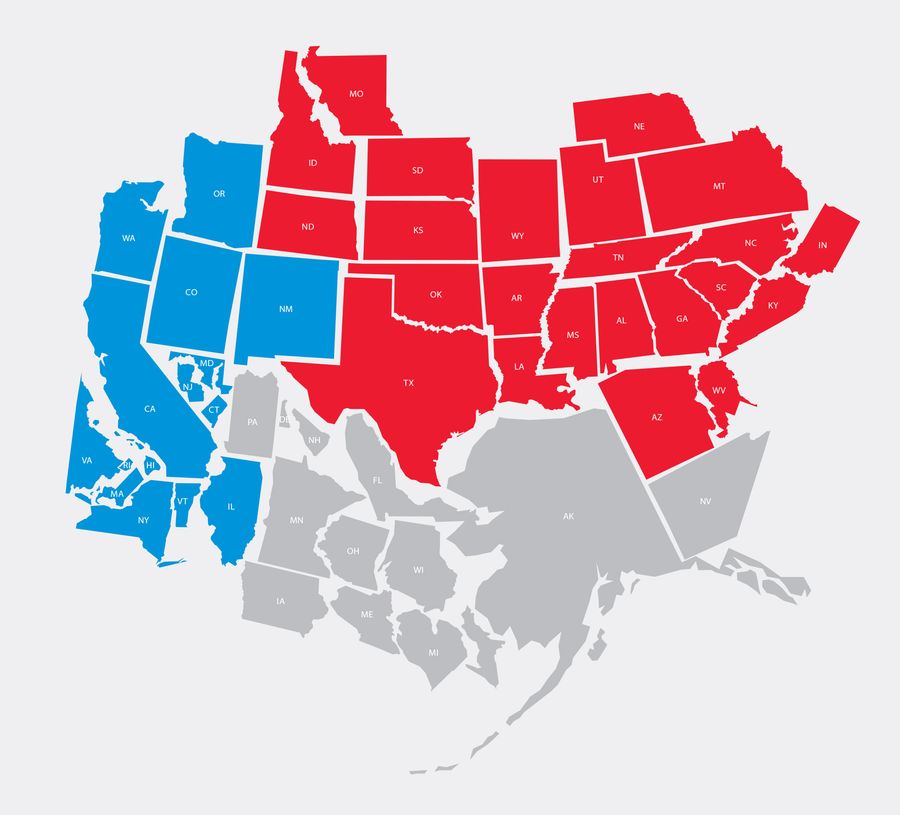
Blue FeBlue Federation (blue), Red Federation (red), and Neutral Federation (gray).
Population
Blue Federation: 128.5 million
Red Federation: 119.2 million
Neutral Federation: 77.3 million
Population by Race
White
Blue: 69,036,422
Red: 73,482,040
Neutral: 64,608,488
Black
Blue: 12,680,587
Red: 17,661,932
Neutral: 8,443,243
Hispanic
Blue: 28,745,227
Red: 18,054,043
Neutral: 8,330,731
Asian
Blue: 11,206,713
Red: 2,984,794
Neutral: 2,210,135
Other
Blue: 4,642,560
Red: 3,709,463
Neutral: 2,102,755
Foreign-Born Population
Blue: Foreign-born: 19.09 percent; U.S.-born: 79.19 percent
Red: Foreign-born: 8.39 percent; U.S.-born: 88.84 percent
Neutral: Foreign-born: 9.79 percent; U.S.-born: 88.12 percent
Unemployment Rate
Blue: 3.89 percent
Red: 3.36 percent
Neutral: 3.59 percent
Income Distribution by Population
$200K+
Blue: 3,652,752
Red: 1,722,633
Neutral: 1,255,983
Under $25K
Blue: 8,966,417
Red: 10,612,524
Neutral: 6,658,590
GDP (billions)
Blue: $8,758,871
Red: $6,210,030
Neutral: $4,181,430
Fortune 500s
Blue: 237
Red: 141
Neutral: 119
Incarcerated Citizens
Blue: 624,225
Red: 927,958
Neutral: 465,229
Percentage of Population Without Health Insurance
Blue: 9.80 percent
Red: 13.63 percent
Neutral: 10.11 percent
Master’s Degree
Blue: 11,759,157
Red: 7,261,992
Neutral: 5,408,654
Tourist Attractions
Blue: Disneyland, Statue of Liberty
Red: Dollywood, Mount Rushmore
Neutral: Disney World, Hersheypark
National Parks
Blue: Yosemite, Rocky Mountain
Red: Yellowstone, Grand Canyon
Neutral: Denali, Everglades
— Reporting by Rachel Bashein
*Figures from the U.S. Census Bureau, the Bureau of Economic Analysis, the Sentencing Project, and Fortune magazine.
No comments:
Post a Comment